
Childhood Illnesses
Childhood illnesses encompass a wide range of conditions that commonly affect children. These illnesses can vary in severity from mild infections to more serious diseases requiring medical intervention. Here are some of the most common childhood illnesses:
- Common Cold: The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. Symptoms include a runny nose, sore throat, cough, and mild fever. It is highly contagious but typically resolves on its own.
- Chickenpox: Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, chickenpox results in a widespread, itchy rash with red spots and blisters. Vaccination has significantly reduced its incidence.
- Measles: A highly contagious viral disease, measles causes a high fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic red rash. Vaccination has made it rare in many parts of the world.
- Ear Infections: Otitis media, or middle ear infection, is common in children and often follows a cold. Symptoms include ear pain, trouble hearing, and sometimes fever.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: This viral illness, usually caused by coxsackievirus, leads to fever, sores in the mouth, and a rash on the hands and feet. It typically affects young children.
- Strep Throat: Caused by group A streptococcus bacteria, strep throat results in a sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. It requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications.
- Influenza: The flu is a viral respiratory illness with symptoms including high fever, cough, body aches, and fatigue. Annual vaccination is recommended for prevention.
- Gastroenteritis: Often referred to as stomach flu, this condition involves inflammation of the stomach and intestines, leading to vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. It is commonly caused by viruses like rotavirus or norovirus.
- Asthma: A chronic condition characterized by airway inflammation, asthma leads to wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. It often requires long-term management with medications.
- RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): This virus causes respiratory infections, particularly in infants and young children. Symptoms range from mild cold-like symptoms to severe bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis): Caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria, this highly contagious disease leads to severe coughing fits followed by a “whooping” sound. Vaccination is crucial for prevention.
- Scarlet Fever: Resulting from a strep throat infection, scarlet fever causes a red, sandpaper-like rash, along with a high fever and sore throat. Antibiotics are used for treatment.
- Mumps: A viral infection that affects the salivary glands, mumps causes swelling and pain in the jaw and cheeks, along with fever and muscle aches. Vaccination has reduced its prevalence.
Preventive measures such as vaccination, good hygiene practices, and regular pediatric check-ups play a vital role in managing and reducing the incidence of these childhood illnesses. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for ensuring the health and well-being of children.

Childhood Infections
Childhood infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites that commonly affect children. Some of the most prevalent childhood infectious diseases include:
- Measles: A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, and a red rash.
- Mumps: A viral infection that causes swelling of the salivary glands, leading to puffy cheeks and a swollen jaw.
- Rubella (German measles): A viral infection with symptoms including a rash, mild fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Chickenpox (Varicella): A highly contagious viral infection causing an itchy rash with red spots and blisters.
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis): A bacterial infection leading to severe coughing spells that can interfere with breathing.
- Polio: A viral disease that can cause paralysis and muscle weakness.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: A viral infection that results in sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
- Scarlet Fever: A bacterial illness that develops in some people who have strep throat, characterized by a red rash, fever, and sore throat.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV): A common virus causing respiratory infections, particularly severe in infants and young children.
- Influenza (Flu): A viral infection that affects the respiratory system, causing fever, cough, and body aches.
Vaccinations have significantly reduced the incidence of many of these diseases, but they still pose a threat in regions with low immunization rates. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing and preventing the spread of these infectious diseases.
Children Vaccinations / Immunisations
Vaccination and Immunization in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune
At Shreevatsa Children's Clinic and Vaccination Centre in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune, we understand the importance of timely vaccinations and immunizations to protect your child from various preventable diseases. Vaccination is a critical component of pediatric care, ensuring your child's health and well-being.
Why Vaccinate?
Vaccinations protect children from serious illnesses such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, hepatitis, and more. Immunization helps in building immunity and prevents the spread of contagious diseases within the community.
Our Vaccination Services
We offer a comprehensive range of vaccination and immunization services tailored to your child's age and health requirements. Our experienced pediatricians ensure that each vaccine is administered safely and efficiently.
Why Choose Us for Vaccinations in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune?
- Experienced Pediatricians*: Our skilled pediatricians ensure that vaccinations are administered safely.
- Comprehensive Care*: We provide a full range of vaccines according to the recommended schedule.Booster Vaccines
- Personalized Attention*: Each child's vaccination plan is tailored to their specific health needs.
- Convenient Location*: Located in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune, our clinic is easily accessible for families in the area.
Adult Vaccinations
Adult vaccinations are essential for maintaining health and preventing the spread of various diseases. Here are some key vaccines recommended for adults:
- Influenza (Flu) Vaccine: Recommended annually for all adults.
- Tdap (Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis) Vaccine: A single dose, followed by a Td (Tetanus, Diphtheria) booster every 10 years.
- MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) Vaccine: For adults without evidence of immunity, especially those born after 1957.
- Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccine: For adults without evidence of immunity.
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus) Vaccine: Recommended for adults up to age 26, and some adults aged 27-45 based on a discussion with their healthcare provider.
- Shingles (Herpes Zoster) Vaccine: Recommended for adults aged 50 and older.
- Pneumococcal Vaccines (PPSV23 and PCV13): For adults 65 and older, and younger adults with certain health conditions.
- Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: For adults at risk or those who want protection from these diseases.
- Meningococcal Vaccines: For adults at risk due to medical conditions, travel, or other factors.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine which vaccines are appropriate for you based on your health history, lifestyle, and travel plans.

Child Nutrition
Nutrition in Children in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune
Welcome to Shreevatsa Children's Clinic and Vaccination Centre, your trusted source for expert advice on child nutrition in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune. Proper nutrition is essential for your child's growth, development, and overall health. Our clinic is dedicated to providing comprehensive nutritional guidance tailored to meet the unique needs of each child.
Importance of Child Nutrition
Good nutrition is the foundation for a healthy life. It supports physical growth, cognitive development, and immune function. Ensuring that your child receives the right balance of nutrients is crucial for their development and well-being.
Our Child Nutrition Services
At Shreevatsa Children's Clinic, we offer a range of nutrition services designed to address various aspects of your child's diet and health. Our experienced pediatricians and nutritionists work closely with families to develop personalized nutrition plans.
Services Offered
- Nutritional Assessments*: Comprehensive evaluations to understand your child’s dietary needs and nutritional status.
- Dietary Planning*: Customized meal plans that ensure a balanced intake of essential nutrients.
- Nutritional Counseling*: Guidance on healthy eating habits, portion control, and dealing with picky eaters.
- Management of Nutritional Deficiencies*: Identification and treatment of deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, and vitamin D.
- Special Dietary Needs*: Support for children with food allergies, intolerances, or specific health conditions requiring dietary modifications.
- Growth Monitoring*: Regular tracking of your child’s growth patterns to ensure they are on the right track developmentally.
Why Choose Us for Child Nutrition Services in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune?
- Experienced Professionals*: Our team includes skilled pediatricians and nutritionists with expertise in child nutrition.
- Personalized Approach*: We create individualized nutrition plans based on your child's unique needs and lifestyle.
- Family-Centered Care*: We involve parents and caregivers in the nutritional planning process to ensure practical and sustainable dietary changes.
- Convenient Location*: Our clinic is conveniently located in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune, making it easily accessible for local families.
Child nutrition issues encompass a range of challenges that can affect children’s health and development. Key issues include:
- Malnutrition: Includes both undernutrition (wasting, stunting, underweight) and overnutrition (obesity). Malnutrition can lead to poor physical and cognitive development and increased susceptibility to diseases.
- Micronutrient Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, iodine, vitamin A, and zinc, can cause significant health problems, including anemia, weakened immune system, and developmental delays.
- Food Insecurity: Limited access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food can impair children’s growth and overall well-being.
- Poor Dietary Practices: Unhealthy eating habits, such as high consumption of sugary, salty, and fatty foods, can lead to obesity and related health issues like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Lack of Education and Awareness: Insufficient knowledge about balanced diets and nutrition can lead to poor food choices and feeding practices.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and inadequate sanitation can exacerbate nutrition issues in children.
Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, including improved access to nutritious foods, education on healthy eating, better healthcare services, and policies that support child nutrition programs.

Nutritional Assessments/Child Growth
Nutritional assessments in children typically involve evaluating their growth patterns, dietary intake, and overall health. Here are some common methods used:
- Anthropometric Measurements: These include height, weight, head circumference (for infants), and body mass index (BMI). Growth charts are used to assess if the child’s growth is normal for their age.
- Dietary Assessment: This involves evaluating the child’s dietary intake, either through a 24-hour recall, food diary, or food frequency questionnaire.
- Clinical Examination: This includes a physical exam to assess signs of malnutrition or nutrient deficiencies, such as muscle wasting, skin changes, or hair texture.
- Biochemical Tests: Blood tests may be done to assess levels of certain nutrients, such as iron, vitamin D, or vitamin B12.
- Developmental Assessment: This evaluates developmental milestones to ensure that nutritional deficiencies are not impacting growth and development.
- Family and Social History: This includes information about the child’s feeding practices, family dynamics, and socioeconomic factors that may affect nutrition.
These assessments are typically performed by healthcare professionals, such as pediatricians, dietitians, or nutritionists, to ensure that children are receiving adequate nutrition for optimal growth and development.

Diet Charts
Creating a balanced diet chart for children is essential to ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and development. Here are some general guidelines for different age groups:
Toddlers (1-3 Years)
Breakfast
- Whole grain cereal with milk
- A piece of fruit or berries
- A small glass of water
Mid-Morning Snack
- A piece of fruit or a small handful of nuts (if not allergic)
Lunch
- A small portion of lean protein (chicken, fish, beans)
- Vegetables (steamed or raw)
- Whole grain bread or rice
- A glass of milk or water
Afternoon Snack
- Yogurt or cheese sticks
- Sliced vegetables or fruit
Dinner
- A small portion of lean protein
- Vegetables
- A serving of whole grains (quinoa, whole wheat pasta)
- A glass of water
Preschoolers (4-5 years)
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with fruit and nuts
- A glass of milk or water
Mid-Morning Snack
- A piece of fruit or a small handful of nuts
Lunch
- Whole grain wrap or sandwich with lean protein and vegetables
- A side of fruit or yogurt
- A glass of water
Afternoon Snack
- Carrot sticks or celery with hummus
- A piece of fruit
Dinner
- A portion of lean protein (grilled chicken, fish, tofu)
- Mixed vegetables
- Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice)
- A glass of water
Adolescents (13-18 years)
Breakfast
- Smoothie with fruit, yogurt, and spinach
- Whole grain toast with peanut butter
Mid-Morning Snack
- A piece of fruit or a small handful of nuts
Lunch
- Salad with lean protein, a variety of vegetables, and a whole grain roll
- A glass of water
Afternoon Snack
- Greek yogurt with berries
- A small handful of nuts or seeds
Dinner
- A portion of lean protein (chicken, fish, legumes)
- Steamed or roasted vegetables
- Whole grains (brown rice, whole wheat pasta)
- A glass of water
General Tips
- Encourage a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Include whole grains over refined grains.
- Offer lean protein sources.
- Limit sugary snacks and beverages.
- Ensure adequate hydration with water.
- Adjust portion sizes based on the child’s age, size, and activity level.
Always consult with a pediatrician or a nutritionist for personalized dietary advice tailored to your child’s specific needs and health conditions.
A well-balanced diet is crucial for kids in sports to support their growth, development, and energy needs. Here are some key considerations:
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for sports and daily activities. Good sources include whole grains (whole wheat bread, oatmeal), fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins: Important for muscle growth and repair. Lean meats (chicken, turkey), fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and nuts are good sources.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for a variety of colors to ensure a range of nutrients.
- Hydration: Proper hydration is essential. Water is the best choice. For intense sports, consider sports drinks with electrolytes, but avoid sugary drinks.
- Healthy Fats: Provide energy and support growth. Include sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and healthy oils (olive oil, canola oil).
- Timing: Encourage regular meals and snacks to maintain energy levels. Avoid heavy meals right before exercise.
- Avoid Sugary and Processed Foods: Limit sugary snacks, fast food, and processed foods. They can lead to energy spikes and crashes.
- Balanced Meals: Include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in each meal and snack to maintain energy levels.
- Consult a Professional: For personalized advice, especially if your child has specific dietary needs or health concerns, consult with a registered dietitian or a pediatrician.
Ensuring your child eats a balanced diet tailored to their activity level can help support their performance and overall health.

Childhood Asthma / Hyper Reactive Airway Disorders
Childhood asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways that affects children. It is characterized by recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing, particularly at night or in the early morning. These symptoms are often triggered by factors such as allergens, respiratory infections, physical activity, cold air, and environmental pollutants.
Key points about childhood asthma:
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These can vary in severity and frequency.
- Triggers: Common triggers include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, tobacco smoke, respiratory infections, physical activity, cold air, and stress.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, and tests such as spirometry to measure lung function. In some cases, allergy testing may be performed.
- Management: Management includes avoiding known triggers, using inhalers (both rescue and controller inhalers), and taking prescribed medications. Education on proper inhaler technique and asthma action plans is crucial.
- Medications: Common medications include short-acting beta-agonists (for quick relief), inhaled corticosteroids (for long-term control), and leukotriene modifiers.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is important to manage and adjust treatment as needed.
- Impact on Daily Life: With proper management, most children with asthma can lead active, normal lives. However, uncontrolled asthma can impact school attendance, physical activity, and overall quality of life.
Early and effective management of asthma in children is essential to prevent severe asthma attacks and ensure better long-term health outcomes.
Inhalation therapy is a cornerstone of asthma management in children due to its effectiveness in delivering medication directly to the lungs. The main types of inhalation devices include:
- Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs): These are small, portable devices that deliver a specific amount of medication in aerosol form. They often require the use of a spacer to ensure proper delivery of the medication to the lungs, especially in young children.
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs): These devices deliver medication in powder form. They are breath-activated, meaning the medication is released when the child inhales through the device. DPIs require a certain level of inspiratory effort, making them suitable for older children who can manage the technique.
- Nebulizers: These convert liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled through a mouthpiece or mask. Nebulizers are often used for younger children or those who have difficulty using MDIs or DPIs.
Medications Used in Inhalation Therapy
- Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs): These are quick-relief medications used to treat acute asthma symptoms. Examples include albuterol and levalbuterol.
- Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS): These are long-term control medications used to reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent asthma symptoms. Examples include budesonide and fluticasone.
- Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs): These are used in combination with ICS for long-term control. Examples include salmeterol and formoterol.
- Combination inhalers: These contain both ICS and LABAs and are used for long-term control. Examples include fluticasone/salmeterol and budesonide/formoterol.
Advantages of Inhalation Therapy
- Direct delivery to the lungs: Inhalation therapy allows medication to be delivered directly to the site of inflammation and bronchoconstriction, providing rapid relief and reducing systemic side effects.
- Lower doses: Because the medication is delivered directly to the lungs, lower doses are required compared to oral medications, which can reduce the risk of side effects.
- Ease of use: Inhalers and nebulizers can be used at home, making them convenient for long-term management of asthma.
Challenges
- Proper technique: Ensuring proper inhaler technique is crucial for the effectiveness of the therapy. This often requires education and regular review by healthcare providers.
- Adherence: Consistent use of inhalation therapy, especially for long-term control medications, can be challenging, particularly in children who may be resistant to regular medication use.
Education and Monitoring
- Training: Parents and children should be trained on the correct use of inhalers and nebulizers. This includes demonstrations and practice sessions.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor asthma control, adjust medication doses, and reinforce proper inhaler technique.
Inhalation therapy remains a fundamental component of asthma management in children, combining efficacy with safety when used correctly.
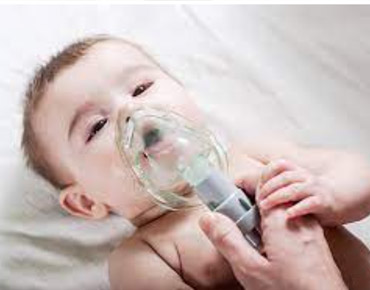
Nebulisations
Nebulisation is a common method of administering medication directly to the lungs in the form of a mist, which is especially useful in children who may have difficulty using inhalers correctly. It is often used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Key Points about Nebulisation in Children:
- Medications: Common medications used in nebulisers include bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol), corticosteroids (e.g., budesonide), and saline solutions. These help to open airways, reduce inflammation, and thin mucus.
- Process: The medication is placed in a nebuliser cup, which is then connected to a mouthpiece or mask. The nebuliser machine converts the liquid medication into a fine mist that the child inhales over several minutes.
- Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Nebulisers are easier for young children and infants to use, as they only need to breathe normally through the mask.
- Disadvantages:
- Effective Delivery: Provides direct delivery of medication to the lungs, which can be more effective and faster-acting than oral medications.
- Time-Consuming: Treatments typically take 10-15 minutes. Equipment Maintenance: Nebulisers require regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure proper function and hygiene.
- Side Effects: Potential side effects can include rapid heart rate, jitteriness, and, rarely, allergic reactions. It’s important to monitor the child during treatment and consult a healthcare provider if any adverse effects occur.
- Usage Tips:
- Calm Environment: Keep the child calm and comfortable during nebulisation. Distractions such as books or videos can help.
- Regular Cleaning: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning the nebuliser to prevent infections.
- Proper Technique: Ensure the mask fits well and the child breathes deeply and evenly to maximize the effectiveness of the medication.
When to Seek Medical Advice:
- If the child shows signs of an allergic reaction (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing).
- If symptoms do not improve or worsen after nebulisation.
- For any questions about the dosage or frequency of nebulisation treatments.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting nebulisation therapy to ensure it is appropriate for the child’s specific condition and to receive proper instructions on its use.

Child Growth / Developmental / Behavioral disorders
Developmental Issues in Children in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune
Welcome to Shreevatsa Children's Clinic and Vaccination Centre, your trusted resource for addressing developmental issues in children in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune. Understanding and addressing developmental and behavioral problems early is crucial for your child’s long-term well-being. Our clinic offers comprehensive evaluations and personalized interventions to support your child's growth and development.
Understanding Developmental Issues
Developmental issues can manifest in various ways, including delays in speech, motor skills, social interactions, and learning abilities. Early identification and intervention are key to helping children overcome these challenges and reach their full potential.
Common Developmental and Behavioral Problems
- Speech and Language Delays*: Difficulties with speaking, understanding, or using language appropriately.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)*: Challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, and communication.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)*: Symptoms include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- Learning Disabilities*: Issues with reading, writing, math, and other academic skills.
- Sensory Processing Disorder*: Difficulty in processing and responding to sensory information.
- Behavioral Disorders*: Problems such as oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) and conduct disorder.
- Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD)*: Delays in motor skills and coordination.
Our Services for Developmental Issues
At Shreevatsa Children's Clinic, we provide a range of services to diagnose, manage, and support children with developmental and behavioral problems. Our experienced team of pediatricians and specialists work together to create a comprehensive care plan for each child.
Services Offered:
- Developmental Assessments*: Thorough evaluations to identify developmental delays and behavioral issues.
- Early Intervention Programs*: Customized intervention plans to address specific developmental challenges.
- Speech and Language Therapy*: Support for children with speech and language delays.
- Occupational Therapy*: Assistance with fine motor skills, sensory processing, and daily living activities.
- Behavioral Therapy*: Techniques to manage and improve behavioral issues.
- Parental Guidance and Support*: Counseling and resources for parents to support their child’s development at home.
- School Readiness Programs*: Preparing children with developmental issues for a successful transition to school.
Why Choose Us for Developmental Issues in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune?
- Experienced Specialists*: Our team includes skilled pediatricians and therapists with expertise in developmental and behavioral issues.
- Comprehensive Care*: We provide a holistic approach to address all aspects of your child’s development.
- Family-Centered Approach*: We involve parents in the assessment and intervention process to ensure the best outcomes.
- Convenient Location*: Our clinic in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune, is easily accessible for local families seeking specialized care.
Childhood developmental disorders are a group of conditions that originate during the developmental period and can impact physical, learning, language, or behavior areas. Here are some of the most common types:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A range of conditions characterized by challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, speech, and nonverbal communication. The spectrum nature means that the symptoms and their severity can vary widely.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Characterized by patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with functioning or development.
- Learning Disabilities: Disorders that affect the ability to understand or use spoken or written language, do mathematical calculations, coordinate movements, or direct attention. Examples include dyslexia, dyscalculia, and dysgraphia.
- Intellectual Disability (ID): Characterized by significant limitations in both intellectual functioning and in adaptive behavior, which covers many everyday social and practical skills.
- Communication Disorders: Include speech disorders and language disorders. Examples are expressive language disorder, receptive language disorder, and phonological disorder.
- Motor Disorders: Include developmental coordination disorder and stereotypic movement disorder. These affect the development and coordination of movement.
- Tic Disorders: Include Tourette syndrome and other conditions where individuals make sudden, repetitive movements or sounds.
- Cerebral Palsy: A group of disorders that affect a person’s ability to move and maintain balance and posture. It is caused by abnormal brain development or damage to the developing brain.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing these disorders effectively. Interventions can include therapy (speech, occupational, physical), special education services, behavioral therapy, and sometimes medication.
Behavioral disorders in children encompass a range of conditions that can significantly impact their emotional and social development. Common types include:
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD): Involves a pattern of angry, irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness.
- Conduct Disorder (CD): Manifests through aggressive behavior, violation of rules, and social norms.
- Anxiety Disorders: Include excessive fear, worry, or shyness that interferes with daily activities.
- Depression: Persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest that affect daily functioning.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Impacts social skills, communication, and behavior, often including repetitive behaviors.
These disorders often require a combination of therapeutic interventions, including behavioral therapy, family therapy, medication, and educational support to manage symptoms and improve the child’s functioning. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better outcomes.
Childhood growth disorders encompass a range of conditions that result in abnormal growth patterns in children. These can manifest as either growth that is too rapid or too slow, and they may be due to various underlying causes, including genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, chronic diseases, nutritional deficiencies, or other medical conditions.
Here are some common types of childhood growth disorders:
- Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD): A condition where the pituitary gland does not produce enough growth hormone, leading to slower growth rates.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can result in slowed growth and development, as thyroid hormones are crucial for normal growth.
- Constitutional Growth Delay: Some children are naturally smaller than their peers but grow at a normal rate and eventually reach a normal adult height. They often have a family history of similar growth patterns.
- Turner Syndrome: A genetic disorder affecting females, characterized by the absence of part or all of a second sex chromosome, leading to short stature and other physical abnormalities.
- Achondroplasia: A form of dwarfism caused by a genetic mutation, resulting in short stature with disproportionate limb lengths.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like chronic kidney disease, heart disease, or gastrointestinal disorders can affect a child’s growth due to the body’s inability to absorb nutrients or due to chronic inflammation.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition can significantly impair a child’s growth and development, often seen in cases of severe malnutrition or eating disorders.
- Psychosocial Dwarfism: A condition where emotional deprivation or extreme stress can inhibit growth hormone production, leading to stunted growth.
Diagnosis of growth disorders typically involves a combination of physical examinations, growth chart analysis, hormonal testing, and imaging studies. Treatment depends on the specific disorder and may include hormone replacement therapy, nutritional support, or treatment of underlying medical conditions. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing these disorders effectively and improving outcomes for affected children.

Breastfeeding and Lactation
Breastfeeding and Lactation Consultation in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune
Welcome to Shreevatsa Children's Clinic and Vaccination Centre, your trusted partner in providing comprehensive breastfeeding and lactation support in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune. Breastfeeding is a vital aspect of your baby's health and development, and our expert team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Importance of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for both mother and baby. It provides essential nutrients, strengthens the baby’s immune system, and fosters a strong emotional bond. Additionally, breastfeeding helps mothers recover post-delivery and reduces the risk of certain diseases.
Our Lactation Consultation Services
At Shreevatsa Children's Clinic, we understand that breastfeeding can come with challenges. Our specialized lactation consultation services are designed to support new mothers through personalized guidance and expert advice.
Services Offered
- Initial Breastfeeding Guidance*: Learn the basics of breastfeeding, including latching techniques, feeding positions, and establishing a feeding routine.
- Lactation Support*: Address common breastfeeding issues such as nipple pain, engorgement, and low milk supply with our professional help.
- Nutritional Advice*: Receive dietary recommendations to ensure you and your baby get the necessary nutrients.
- Pumping and Storage*: Guidance on using breast pumps and storing breast milk safely.
- Weaning*: Assistance with the transition from breastfeeding to solid foods.
Why Choose Us for Breastfeeding and Lactation Consultation in Thergaon, Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune?
- Expert Consultants*: Our team includes certified lactation consultants with extensive experience in helping mothers breastfeed successfully.
- Personalized Care*: We provide individualized consultations tailored to your unique needs and concerns.
- Comfortable Environment*: Our clinic offers a warm and supportive environment where you can feel at ease discussing your breastfeeding journey.
- Follow-Up Support*: Continuous support through follow-up consultations to ensure ongoing breastfeeding success.
Lactation issues can be challenging and vary widely among individuals. Common problems include:
- Low Milk Supply: This can be caused by infrequent breastfeeding, poor latch, or certain medical conditions. Increasing the frequency of breastfeeding or pumping can help, as can ensuring proper latch and positioning.
- Engorgement: When breasts are overly full, they can become hard and painful. Regular breastfeeding or pumping can relieve this, along with warm compresses and gentle massage.
- Mastitis: This is an infection in the breast tissue, often resulting from blocked milk ducts. Symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, and fever. It requires medical treatment, usually antibiotics.
- Sore Nipples: Improper latch, dry skin, or thrush can cause this. Using nipple creams, ensuring a proper latch, and addressing any infections can help.
- Blocked Ducts: These can cause localized pain and swelling. Frequent breastfeeding or pumping, warm compresses, and massage can help clear the blockage.
- Oversupply: Producing too much milk can lead to engorgement, blocked ducts, and discomfort. Feeding from one breast per session or expressing just enough milk for comfort can help manage this.
For persistent issues, consulting a lactation consultant or healthcare provider is advisable. They can provide personalized advice and support.

Child Psychology
Child psychology is the study of the mental, social, and emotional development of children from birth through adolescence. It encompasses a wide range of topics including cognitive development, emotional regulation, social interactions, language acquisition, and the influence of family, school, and culture. Key areas of focus in child psychology include:
- Developmental Stages: Understanding how children progress through various stages of development, such as those proposed by theorists like Jean Piaget (cognitive development) and Erik Erikson (psychosocial development).
- Attachment and Relationships: Exploring the bond between children and their caregivers, and how these early relationships impact later social and emotional development.
- Behavior and Learning: Investigating how children learn, including the roles of reinforcement, punishment, and modeling, as well as the impact of learning disabilities.
- Mental Health: Addressing issues such as anxiety, depression, ADHD, and other mental health concerns that can affect children.
- Socialization: Examining how children learn to interact with others and develop social skills, including the impact of peers, family, and media.
- Parenting and Family Dynamics: Studying the effects of different parenting styles and family structures on child development.
Child psychologists work in various settings, including schools, hospitals, clinics, and private practices, helping to assess and treat developmental issues, emotional problems, and behavioral concerns. They use a range of therapeutic techniques, such as play therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and family therapy, to support children’s mental health and well-being.

Adolescent Illnesses
Adolescent illnesses encompass a range of physical, mental, and behavioral conditions that commonly affect teenagers. Here are some of the most prevalent ones:
Physical Illnesses:
- Asthma: Often starts in childhood and can continue into adolescence.
- Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and adolescents, though Type 2 is becoming more common due to rising obesity rates.
- Mononucleosis: Also known as “mono” or the “kissing disease,” it’s common among teenagers due to its transmission through saliva.
- Obesity: Increasingly prevalent and can lead to other health issues like diabetes and hypertension.
- Acne: A common skin condition during puberty due to hormonal changes.
Mental Health Disorders:
- Depression: Adolescents can suffer from major depressive disorder, often triggered by a combination of genetic, environmental, and social factors.
- Anxiety Disorders: Including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder are particularly common.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Can affect academic performance and social interactions.
Behavioral Issues
- Substance Abuse: Alcohol, tobacco, and drug use can start in adolescence.
- Risky Behaviors: Such as unsafe sexual practices, reckless driving, and violence.
Infectious Diseases
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Including HPV, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.
- Respiratory Infections: Like the flu, especially in communal settings like schools.
Chronic Conditions
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Can begin in adolescence and significantly impact daily functioning.
- Migraines: Severe headaches that can affect school performance and quality of life.
Preventative Care and Management
- Vaccinations: HPV, meningococcal, and Tdap vaccines are important for preventing serious illnesses.
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular health screenings can help detect and manage conditions early.
- Mental Health Support: Counseling and therapy can be crucial for managing mental health disorders.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Encouraging balanced nutrition, physical activity, and sufficient sleep.
Early identification and intervention are crucial in managing these conditions and supporting adolescents’ overall well-being.
Adolescent medicine is a medical subspecialty focused on the care of patients who are in the adolescent period of development, typically ranging from the ages of 10 to 25. This field addresses a wide range of health issues specific to this age group, including:
- Pubertal development and growth
- Reproductive health and contraception
- Mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and eating disorders
- Substance abuse
- Chronic illnesses and their management during adolescence
- Preventive care and health education
Adolescent medicine practitioners often work closely with other specialists to provide comprehensive care that addresses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of adolescent health.

Antenatal Counselling
Antenatal counseling is an important aspect of prenatal care, aimed at providing parents with information, support, and guidance to ensure a healthy pregnancy, prepare for childbirth, and facilitate a smooth transition to parenthood. Here are key components typically covered in antenatal counseling:
Health and Nutrition
- Diet: Importance of a balanced diet, recommended foods, and necessary supplements such as folic acid, iron, and calcium.
- Exercise: Safe exercise routines and benefits of staying active during pregnancy.
- Lifestyle: Avoidance of harmful substances like tobacco, alcohol, and certain medications.
Routine Prenatal Care
- Check-ups: Frequency and importance of regular prenatal visits.
- Screening Tests: Information on routine screenings (e.g., blood tests, ultrasounds) and their purposes.
- Vaccinations: Recommended vaccinations during pregnancy (e.g., flu shot, Tdap).
Understanding Pregnancy Changes
- Physical Changes: Common symptoms and changes in the body during each trimester.
- Emotional Changes: Emotional well-being, mood swings, and the importance of mental health.
Preparation for Childbirth
- Labor and Delivery: Stages of labor, pain relief options, and possible interventions (e.g., C-section).
- Birth Plan: Creating a birth plan, including preferences for labor and delivery.
- Hospital Tour: Familiarizing with the birthing facility and its policies.
Postnatal Care and Infant Care
- Postpartum Recovery: Physical and emotional recovery after childbirth.
- Breastfeeding: Benefits, techniques, and support resources.
- Newborn Care: Basics of newborn care, including feeding, bathing, and sleeping arrangements.
Complications and Risk Factors
- Warning Signs: Recognizing signs of potential complications during pregnancy.
- High-Risk Pregnancies: Special considerations and extra care for high-risk pregnancies (e.g., gestational diabetes, preeclampsia).
Family Planning and Contraception
- Postpartum Contraception: Options and planning for future pregnancies.
- Family Planning: Discussing desired family size and spacing of children.
Emotional Support and Resources
- Support Networks: Importance of support from partners, family, and friends.
- Professional Support: Accessing counseling services, support groups, and educational classes.
Legal and Administrative Information
- Maternity Leave: Understanding rights and benefits related to maternity leave.
- Birth Registration: Procedures for registering the baby’s birth.
Antenatal counseling aims to empower parents with knowledge and confidence, reduce anxiety, and ensure a positive pregnancy and childbirth experience.

Counselling of New Parents
New parents often face a variety of challenges as they adjust to their new roles. Some common issues include:
- Sleep Deprivation: Newborns require frequent feedings and diaper changes, leading to disrupted sleep for parents.
- Feeding: Deciding between breastfeeding and formula feeding, dealing with feeding schedules, and managing feeding difficulties can be stressful.
- Health Concerns: New parents may worry about their baby’s health, including common issues like colic, reflux, and infections.
- Bonding: Building a strong emotional connection with the baby can be a concern, especially if parents are experiencing postpartum depression or anxiety.
- Relationship Strain: The demands of a new baby can put stress on relationships, leading to potential conflicts between partners.
- Lack of Personal Time: Finding time for self-care and personal interests can be challenging, leading to feelings of burnout.
- Balancing Work and Parenting: Returning to work and balancing career demands with parenting responsibilities can be difficult.
- Financial Strain: The costs associated with a new baby, such as medical bills, baby supplies, and childcare, can cause financial stress.
- Advice Overload: New parents often receive conflicting advice from family, friends, and online sources, making it hard to know what’s best for their baby.
- Learning Curve: Figuring out how to care for a baby, including diapering, bathing, and soothing, can be overwhelming for new parents.
Seeking support from family, friends, healthcare providers, and parenting groups can help new parents navigate these challenges.

Newborn baby Care
Caring for a newborn involves several important aspects to ensure the baby’s health and well-being. Here are some key points to consider:
Feeding
- Breastfeeding: Breast milk provides ideal nutrition. Aim to feed every 2-3 hours.
- Formula feeding: If using formula, follow the instructions carefully. Typically, newborns eat every 3-4 hours.
- Burping: Burp your baby during and after feeding to help prevent gas.
Sleeping
- Sleep patterns: Newborns sleep a lot, often 16-17 hours a day, but usually in short stretches.
- Safe sleep environment: Place the baby on their back in a crib with a firm mattress and no loose bedding or toys to reduce the risk of SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome).
stretches
- Safe sleep environment: Place the baby on their back in a crib with a firm mattress and no loose bedding or toys to reduce the risk of SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome).
Diapering
- Frequency: Expect to change diapers frequently, about 8-12 times a day.
- Skin care: Clean the diaper area with each change and use a diaper cream to prevent rashes.
Bathing
- Frequency: 2-3 times a week is sufficient for newborns. More frequent bathing can dry out their skin.
- Safety: Use lukewarm water and a gentle baby soap. Never leave the baby unattended.
Umbilical Cord Care
- Keep the area clean and dry until the stump falls off, which usually takes 1-2 weeks.
- Fold diapers below the stump to keep it dry.
Clothing
- Layers: Dress the baby in layers to keep them warm, but avoid overheating. A general rule is one more layer than you would wear.
- Comfort: Use soft, breathable fabrics.
Health and Safety
- Doctor visits: Regular check-ups with a pediatrician are crucial.
- Immunizations: Keep up with the recommended vaccination schedule.
- Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and ensure others do too before handling the baby.
Comfort and Bonding
- Holding and cuddling: Physical contact is important for emotional bonding.
- Soothing: Swaddling, gentle rocking, and soft singing can help soothe a fussy baby.
Signs to Watch For
- Feeding difficulties: Trouble latching, sucking, or showing disinterest in feeding.
- Sleep issues: Excessive sleepiness or difficulty waking.
- Health concerns: Persistent crying, fever, or unusual behavior should prompt a call to the doctor.

Counselling of child / Adolescent
Child counseling is a type of therapy that focuses on helping children with emotional, behavioral, and psychological issues. Here are some key aspects of child counseling:
- Goals: The primary goals are to help children manage their emotions, improve behavior, and enhance social skills. It also aims to support children in coping with family issues, trauma, and stress.
- Techniques: Therapists use various techniques such as play therapy, art therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and talk therapy, tailored to the child’s age and developmental level.
Common Issues Addressed:
- Anxiety and depression
- ADHD and other behavioral disorders
- Family changes like divorce or separation
- Trauma and abuse
- Social difficulties and bullying
- Grief and loss
- Role of Parents: Parental involvement is often crucial. Therapists may work with parents to provide strategies and support to help the child at home.
- Environment: Sessions are typically conducted in a safe, supportive, and child-friendly environment to make the child feel comfortable and secure.
If you have specific questions or need more detailed information, feel free to ask!
Adolescent counseling involves providing support and guidance to teenagers as they navigate the unique challenges of this developmental stage. The goals of adolescent counseling can include:
- Emotional Support: Helping adolescents manage stress, anxiety, depression, and other emotional issues.
- Behavioral Guidance: Assisting in developing healthy behaviors and coping mechanisms.
- Academic Support: Addressing school-related issues, such as academic pressure, learning difficulties, and time management.
- Social Skills: Improving communication skills and helping adolescents build healthy relationships with peers and family.
- Identity Formation: Supporting the exploration of self-identity, values, and future goals.
- Crisis Intervention: Providing immediate support during crises such as bullying, family conflict, or substance abuse.
Counselors typically use a variety of therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), talk therapy, and family therapy, tailored to the individual needs of the adolescent.

Video Call Consultations
Video call consultations for children have become increasingly popular, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. These virtual visits can be beneficial for various reasons:
- Convenience: Families can avoid travel and waiting times.
- Access to Specialists: Easier access to pediatric specialists who may not be available locally.
- Safety: Reduces the risk of exposure to contagious diseases.
- Comfort: Children may feel more at ease in their home environment.
However, there are also challenges, such as ensuring a stable internet connection, managing technical issues, and the limited ability to perform physical examinations. Telehealth can be particularly effective for follow-up visits, mental health consultations, and minor illnesses or concerns. For more serious issues, an in-person visit might still be necessary.

Speech Therapy
Speech therapy for children focuses on diagnosing and treating speech and language disorders. It aims to help children develop effective communication skills. Here are key aspects of speech therapy for children:
- Evaluation: A speech-language pathologist (SLP) assesses the child’s speech, language, cognitive-communication, and oral/feeding/swallowing skills to determine the nature and extent of the disorder.
- Treatment Plans: Based on the evaluation, the SLP creates a personalized treatment plan that may involve exercises to improve articulation, language development, fluency, and voice modulation.
- Techniques and Activities:
- Articulation Therapy: Focuses on correcting specific sounds and syllables.
- Language Intervention Activities: Enhances vocabulary, sentence formation, comprehension, and conversational skills through play, books, and interactive activities.
- Oral Motor/Feeding Therapy: Strengthens the muscles of the mouth for speech and eating.
- Fluency Therapy: Helps children who stutter to improve their speech fluency.
- Parent and Caregiver Involvement: Involves training and educating parents to continue therapy activities at home, ensuring consistent progress.
- Goals: The ultimate goal is to enhance the child’s ability to communicate effectively in various settings, improving their social and academic interactions.
Early intervention is crucial as it can significantly impact a child’s developmental trajectory and overall quality of life.

Pathology
Pathology tests in children can cover a wide range of investigations depending on the symptoms or conditions being evaluated. Common pathology tests for children include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for anemia, infections, and other disorders.
- Blood Chemistry Panel: Measures levels of electrolytes, blood glucose, and other chemicals in the blood.
- Urinalysis: Checks for urinary tract infections, kidney problems, or diabetes.
- Stool Tests: To detect infections or digestive problems.
- X-rays and Imaging: To diagnose bone fractures, infections, or other conditions.
- Allergy Tests: To identify allergies to specific foods, environmental factors, or medications.
- Genetic Tests: To identify genetic disorders or conditions.
These tests help diagnose and monitor various health conditions in children, and their necessity is determined by a pediatrician based on the child’s symptoms and medical history.
Radiology
Radiology for children, often called pediatric radiology, focuses on imaging techniques that are safe and appropriate for children. It includes X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans tailored to meet the unique needs of pediatric patients, taking into account their smaller size and higher sensitivity to radiation.

Child Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy for children involves specialized care to promote physical development, improve movement, and address conditions affecting muscles and joints. It can help with issues like developmental delays, cerebral palsy, sports injuries, and post-surgical recovery, focusing on exercises, stretches, and activities tailored to the child’s needs. We have a team comprising of child physiotherapist
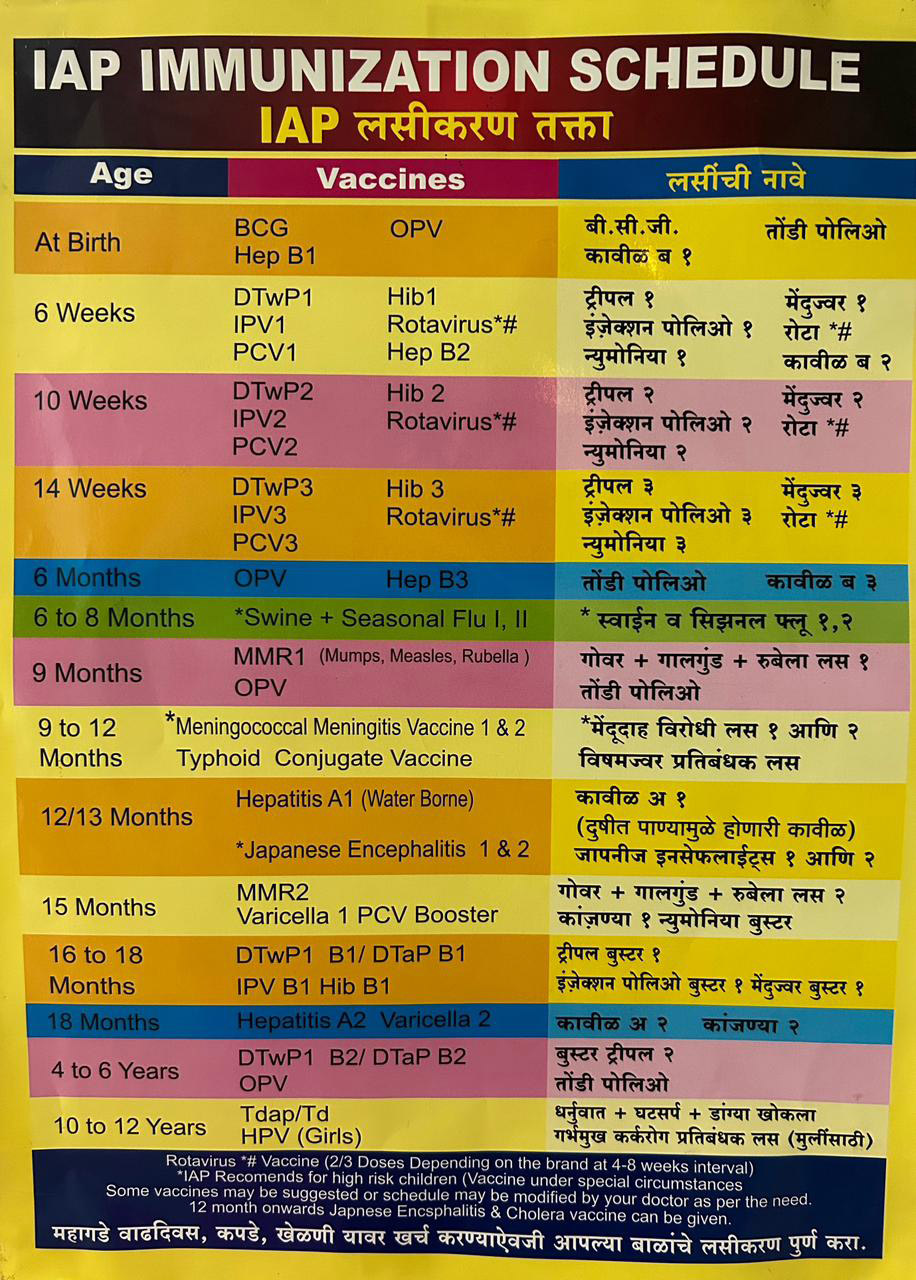
IAP Immunization Schedule
Catch-up vaccination refers to the process of providing vaccinations to individuals who have missed one or more doses of their recommended immunizations at the appropriate ages. This can apply to children, adolescents, and adults who have not received vaccinations according to the standard immunization schedule.
Key aspects of catch-up vaccination include:
- Assessment of Vaccination History: Reviewing the individual’s vaccination records to determine which vaccines are missing or incomplete.
- Prioritization: Identifying which vaccines are most critical based on age, health status, and potential exposure to diseases.
- Scheduling: Creating a schedule to administer the missed vaccines in a timely manner without compromising safety or effectiveness.
- Education: Informing individuals and caregivers about the importance of completing the vaccination series and the potential risks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Follow-up: Ensuring that all subsequent doses are received according to the catch-up schedule.
Catch-up vaccination is important to ensure community immunity and to protect individuals from preventable diseases. It can be particularly crucial in situations where people have moved between regions with different vaccination practices or have had disruptions in their healthcare access.
Vaccinations for travelers depend on the destination and the specific health risks present there. Here are some common vaccinations recommended for travelers:
Routine Vaccinations: Ensure you are up-to-date on routine vaccinations such as:
- MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella)
- DTP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis)
- Varicella (Chickenpox)
- Polio
- Influenza
Travel-Specific Vaccinations:
- Hepatitis A: Recommended for most travelers to regions with poor sanitation.
- Hepatitis B: Advised for travelers to areas with high rates of hepatitis B, especially if engaging in activities that increase risk.
- Typhoid: Suggested for those traveling to areas where typhoid fever is prevalent.
- Cholera: Recommended for areas with active cholera transmission, especially for aid workers or travelers in remote areas.
- Yellow Fever: Required or recommended for travel to certain parts of Africa and South America. Proof of vaccination might be required for entry.
- Japanese Encephalitis: Suggested for extended stays in rural areas of Asia or for those visiting during transmission seasons.
- Rabies: Advised for travelers engaging in activities that may bring them into contact with animals or traveling to regions where rabies is common.
- Meningococcal Meningitis: Required for travelers to certain parts of Africa and for Hajj pilgrims to Saudi Arabia.
Other Considerations:
- Malaria Prophylaxis: While not a vaccine, travelers to malaria-endemic regions should consider taking anti-malarial medication.
- COVID-19: Ensure you are vaccinated and up-to-date with boosters as required by your destination.
Always consult with a healthcare provider or a travel clinic several weeks before your trip to ensure you have enough time to receive the necessary vaccinations and health advice.
Vaccination after an injury is typically related to preventing tetanus. If you sustain a wound, especially a deep puncture wound, animal bite, or any injury involving dirt or rust, you might need a tetanus shot. It’s important to ensure your tetanus vaccination is up to date (usually within the last 10 years). If you haven’t had a booster shot within that timeframe, a doctor may recommend one after such an injury. Always consult a healthcare professional for advice specific to your situation.
